Abstract
Calcined aluminas are generally obtained from Bayer process gibbsite -Al(OH)3, thermal decomposition of which follows the transition through the generic gamma alumina phases to -alumina (corundum), -Al2O3. Calcination of gibbsite has been done in rotary kilns for many years. Specialty calcined aluminas can also be prepared in stationary or fluid bed calciners. Most ceramic grade aluminas are supplied dry ground to about 95% 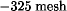 (44 µm) using 85–90% Al2O3 ceramic ball, attrition, vibro-energy, or fluid-energy milling. More fully ground, or superground, calcined aluminas having particle size distributions that approximate the natural or ultimate crystal size of the Bayer grain as calcined are often desired. Thermally reactive aluminas contain submicrometer crystals. These must be separated from the Bayer agglomerate during grinding to permit dense compaction upon ceramic forming, and thus, enhance densification upon sintering at lower temperatures. Process control techniques permit production of calcined specialty aluminas having controlled median particle sizes differentiated by about 0.5 µm. This broad selection enables closer shrinkage control of high tech ceramic parts. Tabular alumina is a high density, high strength form of -Al2O3 made by sintering an agglomerated shape of ground, calcined alumina. It is available in the form of smooth balls which are crushed, screened, and ground to obtain a wide variety of graded, granular, and powdered products. Tabular alumina is the ideal base material for high alumina brick, and monolith liners in the metal, ceramic, and petrochemical industries. Other applications include their use in electrical insulators, electronic components, and kiln furniture. High purity calcium aluminate cements (CAC) are primarily used as binders for high strength refractory castables to form linings up to about 1.0 m thick, as in iron blast furnaces. The high purity CAC finds extensive use as an efficient binder for other aggregates such as fire clays, kaolin, andalusite, kyanite, pyrophyllite, sillimanite, mullite, and refractory-grade bauxite. The many applications cited for tabular alumina in refractories are also common for high purity CAC.
(44 µm) using 85–90% Al2O3 ceramic ball, attrition, vibro-energy, or fluid-energy milling. More fully ground, or superground, calcined aluminas having particle size distributions that approximate the natural or ultimate crystal size of the Bayer grain as calcined are often desired. Thermally reactive aluminas contain submicrometer crystals. These must be separated from the Bayer agglomerate during grinding to permit dense compaction upon ceramic forming, and thus, enhance densification upon sintering at lower temperatures. Process control techniques permit production of calcined specialty aluminas having controlled median particle sizes differentiated by about 0.5 µm. This broad selection enables closer shrinkage control of high tech ceramic parts. Tabular alumina is a high density, high strength form of -Al2O3 made by sintering an agglomerated shape of ground, calcined alumina. It is available in the form of smooth balls which are crushed, screened, and ground to obtain a wide variety of graded, granular, and powdered products. Tabular alumina is the ideal base material for high alumina brick, and monolith liners in the metal, ceramic, and petrochemical industries. Other applications include their use in electrical insulators, electronic components, and kiln furniture. High purity calcium aluminate cements (CAC) are primarily used as binders for high strength refractory castables to form linings up to about 1.0 m thick, as in iron blast furnaces. The high purity CAC finds extensive use as an efficient binder for other aggregates such as fire clays, kaolin, andalusite, kyanite, pyrophyllite, sillimanite, mullite, and refractory-grade bauxite. The many applications cited for tabular alumina in refractories are also common for high purity CAC.
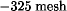 (44 µm) using 85–90% Al
(44 µm) using 85–90% Al