Abstract
The CAS registry lists 5037 aluminum-containing compounds exclusive of alloys and intermetallics. The aluminum containing compound having the largest worldwide market is metal-grade alumina. Second is aluminum hydroxide. Bauxite is the principal ore used for alumina production. Additive applications include those as flame retardants in products such as carpets, and to enhance the properties of paper, plastic, polymer, and rubber products. Significant quantities are also used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, adhesives, polishes, dentifrices, and glass. Aluminum sulfate, 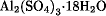 , also known as alum cake, is industrially produced for major applications as a sizing agent in the paper industry and as a coagulant to clarify municipal and industrial water supplies. In terms of worldwide production, it ranks third behind alumina and aluminum hydroxide. All the halogens form covalent aluminum compounds having the formula AlX3. The most important commercially are the anhydrous chloride and fluoride, and aluminum chloride hexahydrate. The latter is used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics as a flocculant and for impregnating textiles. The alkyls and aryls, R3Al (in monomer form), are colorless liquids or low melting solids easily oxidized and hydrolyzed when exposed to the atmosphere. Triethylaluminum (TEA), one of the most commercially important members of this family of chemicals, is so reactive it bursts into flame on contact with air, ie, it is pyrophoric, and it reacts violently with water. Special techniques are necessary for the safe handling and use of organoaluminum compounds, which are used commercially in multimillion kg/yr quantities as catalysts or starting materials for the manufacture of organic compounds such as plastics, elastomers biodegradable detergents, and organometallics containing zinc, phosphorus, or tin. Sodium aluminate is used in water purification, in the paper industry, for the after-treatment of TiO2 pigment, and in the manufacture of aluminum-containing catalysts and zeolite. A large and growing industrial use of aluminum hydroxide and sodium aluminate is the manufacture of synthetic zeolite. Zeolites are aluminosilicates with Si/Al ratios between 1 and infinity. There are 40 natural, and over 100 synthetic, zeolites. Zeolite-based materials are extremely versatile: uses include detergent manufacture, ion-exchange resins (ie, water softeners), catalytic applications in the petroleum industry, separation processes, and as an adsorbent for water, carbon dioxide, mercaptans, and hydrogen sulfide.
, also known as alum cake, is industrially produced for major applications as a sizing agent in the paper industry and as a coagulant to clarify municipal and industrial water supplies. In terms of worldwide production, it ranks third behind alumina and aluminum hydroxide. All the halogens form covalent aluminum compounds having the formula AlX3. The most important commercially are the anhydrous chloride and fluoride, and aluminum chloride hexahydrate. The latter is used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics as a flocculant and for impregnating textiles. The alkyls and aryls, R3Al (in monomer form), are colorless liquids or low melting solids easily oxidized and hydrolyzed when exposed to the atmosphere. Triethylaluminum (TEA), one of the most commercially important members of this family of chemicals, is so reactive it bursts into flame on contact with air, ie, it is pyrophoric, and it reacts violently with water. Special techniques are necessary for the safe handling and use of organoaluminum compounds, which are used commercially in multimillion kg/yr quantities as catalysts or starting materials for the manufacture of organic compounds such as plastics, elastomers biodegradable detergents, and organometallics containing zinc, phosphorus, or tin. Sodium aluminate is used in water purification, in the paper industry, for the after-treatment of TiO2 pigment, and in the manufacture of aluminum-containing catalysts and zeolite. A large and growing industrial use of aluminum hydroxide and sodium aluminate is the manufacture of synthetic zeolite. Zeolites are aluminosilicates with Si/Al ratios between 1 and infinity. There are 40 natural, and over 100 synthetic, zeolites. Zeolite-based materials are extremely versatile: uses include detergent manufacture, ion-exchange resins (ie, water softeners), catalytic applications in the petroleum industry, separation processes, and as an adsorbent for water, carbon dioxide, mercaptans, and hydrogen sulfide.
Keywords: bauxite; Aluminum hydroxide; alumina; aluminum; bayer process; aluminum sulfate; aluminum chloride zealetes; organoaluminum compounds; sodium aluminates
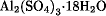 , also known as alum cake, is industrially produced for major applications as a sizing agent in the paper industry and as a coagulant to clarify municipal and industrial water supplies. In terms of worldwide production, it ranks third behind alumina and aluminum hydroxide. All the halogens form covalent aluminum compounds having the formula AlX
, also known as alum cake, is industrially produced for major applications as a sizing agent in the paper industry and as a coagulant to clarify municipal and industrial water supplies. In terms of worldwide production, it ranks third behind alumina and aluminum hydroxide. All the halogens form covalent aluminum compounds having the formula AlX