Abstract
The chemical element calcium, Ca, atomic number 20, is an alkaline-earth metal which is fifth in abundance among all elements (ca 4%) and the third most abundant metal found in the earth's crust. It is too reactive to be found naturally in the free state, but its compounds are widespread as the minerals marble, CaCO3, limestone, CaCO3, calcite, CaCO3, dolomite, 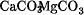 , gypsum,
, gypsum, .gif) , anhydrite, CaSO4, fluorspar, CaF2, fluorapatite, Ca5F(PO4)3, hydroxylapatite, Ca5OH(PO4)3, selenite,
, anhydrite, CaSO4, fluorspar, CaF2, fluorapatite, Ca5F(PO4)3, hydroxylapatite, Ca5OH(PO4)3, selenite, .gif) , and anorthite, CaAl2Si2O8. Lime stone calcium carbonate, is the most widely used of all rocks, as such for dimension stone or aggregate in concrete and road building, or as an industrial chemical and precursor of lime and hydrated lime. More than 90% of the lime consumed in the United States is used for basic or industrial chemistry. It is produced by thermal decomposition (calcination) of calcium carbonate. The hydrolysis process, ie, reaction with water, for lime is called slaking and produces hydrated lime, Ca(OH)2. Calcium hydroxide is a strong base but it finds widespread industrial application as an alkali because it is cheaper than sodium hydroxide. Lime and hydrated lime are used in mortar, treatment of industrial wastes, and treatment of municipal and industrial water supplies. Fluorospar, CaF2, is used as a flux in metallurgical processes such as production of steel in the open-hearth furnace. Calcium hypochlorite, Ca(OCl)2, bleaching agent, in contrast to bleaching powder, does not decompose on standing. Calcium sulfate occurs in large deposits as CaSO4, and as gypsum,
, and anorthite, CaAl2Si2O8. Lime stone calcium carbonate, is the most widely used of all rocks, as such for dimension stone or aggregate in concrete and road building, or as an industrial chemical and precursor of lime and hydrated lime. More than 90% of the lime consumed in the United States is used for basic or industrial chemistry. It is produced by thermal decomposition (calcination) of calcium carbonate. The hydrolysis process, ie, reaction with water, for lime is called slaking and produces hydrated lime, Ca(OH)2. Calcium hydroxide is a strong base but it finds widespread industrial application as an alkali because it is cheaper than sodium hydroxide. Lime and hydrated lime are used in mortar, treatment of industrial wastes, and treatment of municipal and industrial water supplies. Fluorospar, CaF2, is used as a flux in metallurgical processes such as production of steel in the open-hearth furnace. Calcium hypochlorite, Ca(OCl)2, bleaching agent, in contrast to bleaching powder, does not decompose on standing. Calcium sulfate occurs in large deposits as CaSO4, and as gypsum, .gif) . The dihydrate is a functional additive in Portland cement to control setting time. Industrial phosphates including phosphate fertilizers, phosphoric acid, and calcium phosphates are obtained from the large deposits of fluorapatite found in Florida in the United States, and in Morocco. Calcium magnesium acetate (CMA), suggested formula CaMg2(C2H3O2)6, is an emerging bulk chemical. Calcium hydride, CaH2, is an effective reducing agent at high temperatures and has been used to reduce inorganic oxides to their metals. Ordinary glass, soda-lime glass, is a complex mixture of silicates, chiefly those of sodium and calcium. Portland cement is obtained by calcining a mixture of substances to produce an appropriate ratio of the oxides CaO, MgO, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and SiO2. The chief raw materials of ceramic manufacture are clay, feldspar, and sand. Calcium ion shows some tendency to form complexes mainly through coordination with oxygen-containing ligands. Calcium carbide is used to produce calcium cyanamide, CaCN2 (lime nitrogen), used as a fertilizer. Calcium cyanamide can be converted to calcium cyanide, used in cyanidation of metallic ores and production of sodium cyanide and ferrocyanides. Calcium cyanamide has also been used to make cyanamide, which in turn is the starting material for important industrial organic syntheses. Calcium hydride, CaH2, and anhydrous calcium sulfate (Drierite), CaSO4, are useful as drying agents. Biological functions of Ca(II) ion are numerous but may be classified in one of three categories: the formation of solid skeletal material such as bone, teeth, and shell; the stabilizing of protein conformation structure; and the most varied, the ability of Ca(II) to trigger certain physiological activities such as muscle contraction and the release of hormones. The recommended daily allowances of calcium are for children to 10 years of age, 360–800 mg; teenage children, 1200 mg; adults, 800 mg, increasing to 1200 mg during pregnancy and lactation. Cow's milk supplies ca 1.27 g/L of calcium in available form.
. The dihydrate is a functional additive in Portland cement to control setting time. Industrial phosphates including phosphate fertilizers, phosphoric acid, and calcium phosphates are obtained from the large deposits of fluorapatite found in Florida in the United States, and in Morocco. Calcium magnesium acetate (CMA), suggested formula CaMg2(C2H3O2)6, is an emerging bulk chemical. Calcium hydride, CaH2, is an effective reducing agent at high temperatures and has been used to reduce inorganic oxides to their metals. Ordinary glass, soda-lime glass, is a complex mixture of silicates, chiefly those of sodium and calcium. Portland cement is obtained by calcining a mixture of substances to produce an appropriate ratio of the oxides CaO, MgO, Al2O3, Fe2O3, and SiO2. The chief raw materials of ceramic manufacture are clay, feldspar, and sand. Calcium ion shows some tendency to form complexes mainly through coordination with oxygen-containing ligands. Calcium carbide is used to produce calcium cyanamide, CaCN2 (lime nitrogen), used as a fertilizer. Calcium cyanamide can be converted to calcium cyanide, used in cyanidation of metallic ores and production of sodium cyanide and ferrocyanides. Calcium cyanamide has also been used to make cyanamide, which in turn is the starting material for important industrial organic syntheses. Calcium hydride, CaH2, and anhydrous calcium sulfate (Drierite), CaSO4, are useful as drying agents. Biological functions of Ca(II) ion are numerous but may be classified in one of three categories: the formation of solid skeletal material such as bone, teeth, and shell; the stabilizing of protein conformation structure; and the most varied, the ability of Ca(II) to trigger certain physiological activities such as muscle contraction and the release of hormones. The recommended daily allowances of calcium are for children to 10 years of age, 360–800 mg; teenage children, 1200 mg; adults, 800 mg, increasing to 1200 mg during pregnancy and lactation. Cow's milk supplies ca 1.27 g/L of calcium in available form.
Keywords: Calcium compounds; Calcium carbonate; Lime; Hydrated lime; Industrial wastes; treatment; Coordination chemistry; Calcium; Organic chemistry; Water supplies; treatment; Metallurgy; Biological function
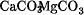 , gypsum,
, gypsum, .gif) , anhydrite, CaSO
, anhydrite, CaSO.gif) , and anorthite, CaAl
, and anorthite, CaAl.gif) . The dihydrate is a functional additive in Portland cement to control setting time. Industrial phosphates including phosphate fertilizers, phosphoric acid, and calcium phosphates are obtained from the large deposits of fluorapatite found in Florida in the United States, and in Morocco. Calcium magnesium acetate (CMA), suggested formula CaMg
. The dihydrate is a functional additive in Portland cement to control setting time. Industrial phosphates including phosphate fertilizers, phosphoric acid, and calcium phosphates are obtained from the large deposits of fluorapatite found in Florida in the United States, and in Morocco. Calcium magnesium acetate (CMA), suggested formula CaMg